fungi life cycle explained
Mature mycelium In reality there are many sub-steps of the process. Fungi are subdivided on the basis of their life cycles the presence or structure of their fruiting body and the arrangement of and type of spores reproductive or distributional cells they produce.

Plasmogamy An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
They exhibit the phenomenon of alternation of generation.

. They even make chemicals like alkaloids. Edible and Poisonous Fungi Edible fungi Field mushrooms truffles honey rot Poisonous fungi Death Cap destroying angel. Under favourable climatic conditions the asexual stage may be repeated resulting in the production of conidia in profuse quantities.
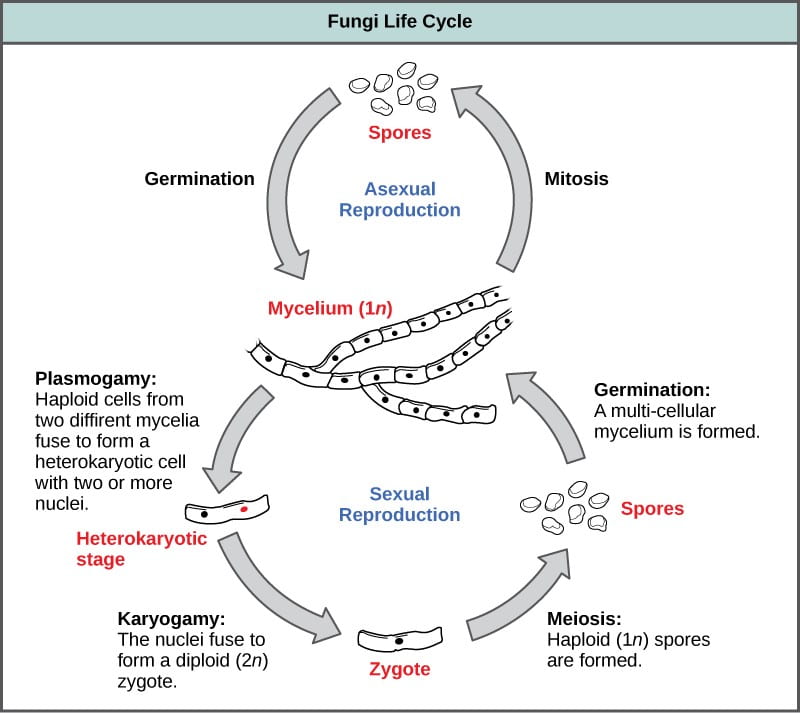
Life cycle of fungi In the life cycle of a sexually reproducing fungus a haploid phase alternates with a diploid phase. The organism is haploid and has no diploid phase except for the sexual sporangium. Some fungal colonies can grow for a very long time and over a very large area.
Identify and describe the key adaptations unique to fungi cell walls made of chitin and external digestion including morphological life cycle and metabolic traits. But that isnt all they do. The haploid phase ends with nuclear fusion and the diploid phase begins with the formation of the zygote the diploid cell resulting from fusion of two haploid sex cells.
Fungi life cycle explained Sunday March 13 2022 Edit. The genus Taphrina old generic name Exoascus still in use by many authors contains several species which are very important pathogens. Explain ecosystem services of fungi and human nutrition applications.
The life cycle inventory phase involves the compilation of elementary flow data ie flows that pass. Fungi can dissolve minerals like phosphorus from rocks and soil converting it to forms that plants can use for food. Fungi reproduce sexually either through cross- or self-fertilization.
While some fungi reproduce sexually others reproduce asexually. Fungi are eukaryotic non-vascular non-motile and heterotrophic organisms. Fungi store their food in the form of starch.
Many fungi need two of these colonies to grow next to each other and to mate before that fungus is able to form any new spores and so spread further. We have summarized them in the fungi life cycle diagram below. They induce hypertrophic malformations of buds leaves twigs flowers and fruits producing.
Life Cycle of Fungi. In this article we will discuss about the life cycle of taphrina explained with the help of suitable diagrams. Fungi replicate sexually andor asexually.
Time which could partially explain Santas association with flying reindeer. Fungi need to produce so many spores because most spores simply die where they land lacking water and food. But this model provides a good overview in terms of how fungi grows from birth to death.
Life Cycle of Fungi Some of the characteristic features of fungi are. Fungi life cycle explained Wednesday March 2 2022 Edit. Macroscopic filamentous fungi that form large fruiting bodies.
Div1 Div1 Fungi Microbiology Fungus Reproduction Youtube Characteristics Of Fungi Boundless Biology Life Cycle Of A Mushroom Worldkids 24 3b Zygomycota The Conjugated Fungi Biology Libretexts. They lack chlorophyll and thus are incapable of photosynthesis. They are eukaryotic non-vascular non-motile and heterotrophic organisms.
They may be unicellular or filamentous. The mushroom life span varies between fungi species. There are four basic steps in the life cycle of a fungi.
The life cycle of a mushroom begins and ends through five stages of evolutionary phases beginning as a fungal spore seeds and completing its cycle as a mature fruiting body the part of a mushroom we all identify and know that releases new spores to create a new cycle all over again. Describe the symbiotic relationship of fungi with plants and pathological relationships with other organisms. When fungi associate with plants and animals the fungi can donate water minerals or nutrients in exchange for the energy the calories they need to grow.
But this model provides a good overview in terms of how fungi grows from birth to death. The stage during which a fungus reproduces asexually is known as asexual stage or asexual cycle or conidial stage or imperfect stage. Life Cycle of Rhizopus.
The term inoculation refers to the spores landing upon and infiltrating a growth medium sometimes known as a substrate. The three major groups of fungi are. If this is a.
They reproduce by means of spores. In this guide we explain the key features of some common mushrooms and provide a brief overview of the fungi life cycle. Most of the ecology of the soil will die the plants do ok in the short run as they are able to absorb from the dead bacteria and fungi but it is a slow cycle of death.
There are four basic steps in the life cycle of a fungi. Brundrett 1990 showed the same cycle pattern using an alternative diagram of the developmental stages of a mould.

24 1c Fungi Reproduction Biology Libretexts

Intro To The Fungi Life Cycle Plantsnap
.PNG)
Ascomycota Cup Fungi Life Cycle

Characteristics Of Fungi Openstax Biology 2e
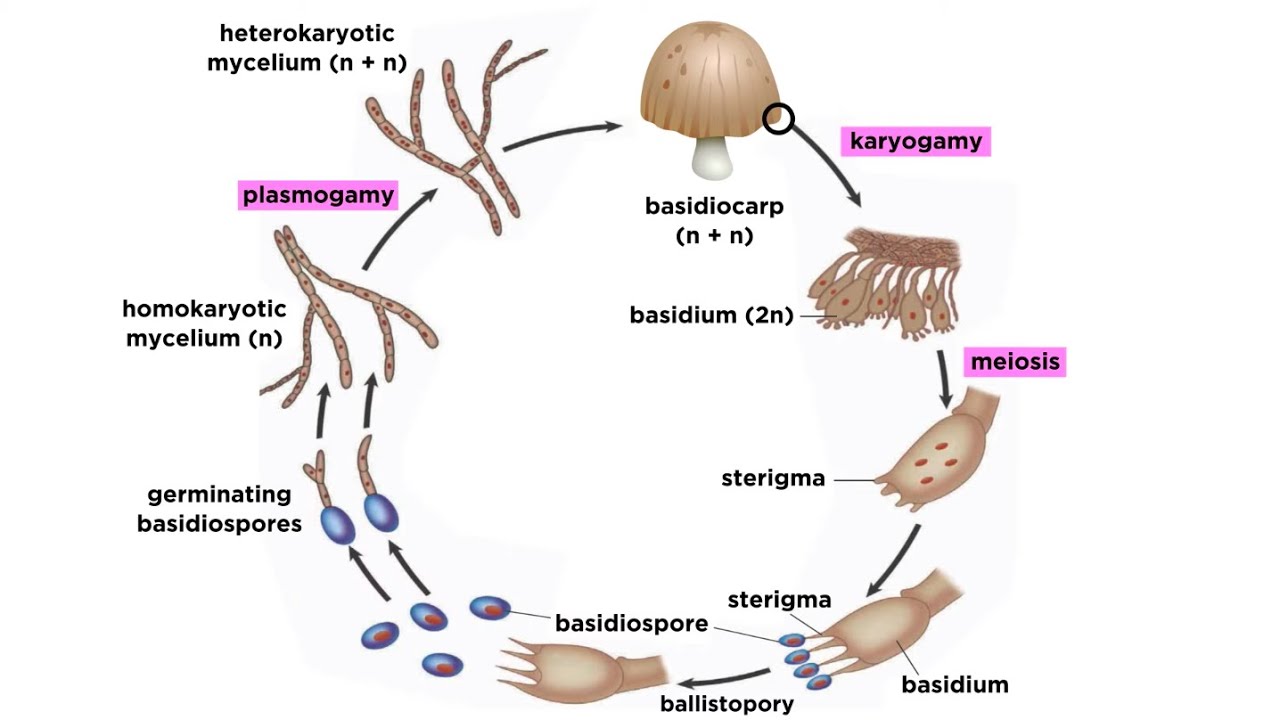
Basidiomycota Part 2 The Mushroom Life Cycle Youtube
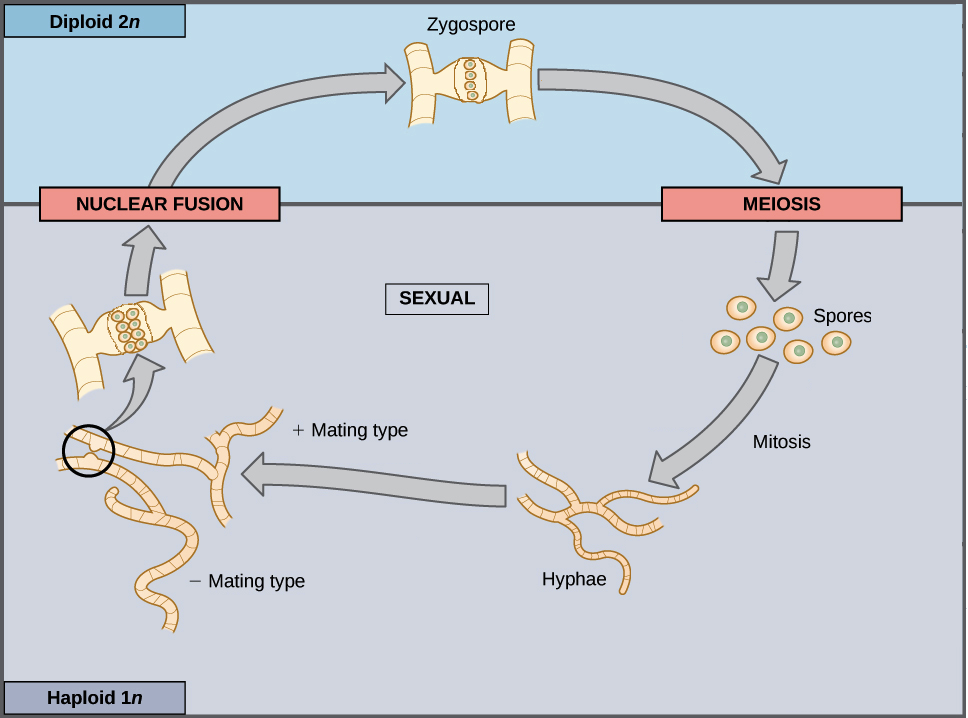
Sexual Life Cycles Article Meiosis Khan Academy

Figure 2 From Entomopathogenic Fungi As An Important Natural Regulator Of Insect Outbreaks In Forests Review Semantic Scholar

Fungi Life Cycle In Basidiomycetes Youtube
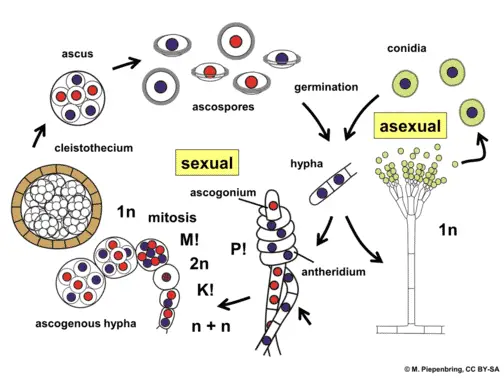
Fungi Explained Here Is What You Need To Know Microscope Clarity

Life Cycle Of A Mushroom Worldkids

Plasmogamy An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
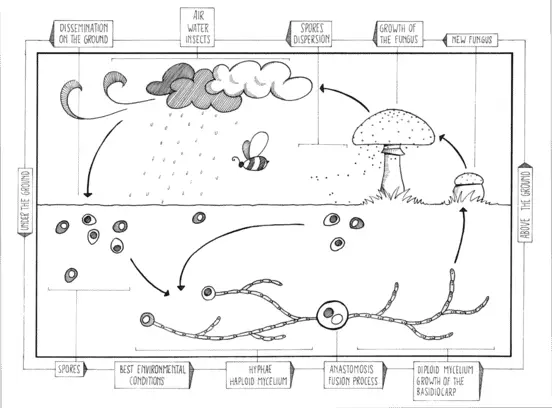
Fungi Explained Here Is What You Need To Know Microscope Clarity

Reproduction In Fungi Life Cycle Of Fungi Youtube

Diagrammatic Representation Of Mushroom Life Cycle Download Scientific Diagram